The Rise of Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a digital payment system, which was developed by an anonymous programmer or group of programmers who identify under the name of Satoshi Nakamoto. Even though the origin of bitcoins remains ambiguous, bitcoin emerged as a cryptocurrency, in which strong algorithm encryptions were used to secure transactions in a different way. This system maintains the identity of its users anonymous or shielded by pseudonyms under a decentralized system where no one is in charge, neither the governments nor the banks, nor Nakamoto.
Bitcoin is a system of peer-topeer networking which uses instant and private transactions. This enables users to make direct payments from one party to another without the involvement of a financial institution. The users can make transactions via a bitcoin wallet, which is a downloadable app on both computers and mobile devices. These transactions are stored in a public ledger known as a blockchain, where the entire bitcoin network relies. Blockchain can either be private with restricted membership or public, thus reachable to anyone.
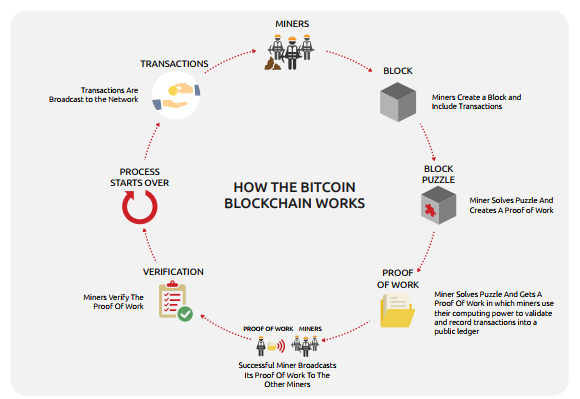
The Bitcoin Game
In the traditional banking system, central banks print or issue money based on the corresponding economic needs. However, this is not the case with bitcoins. Bitcoins are generated through a more complex system known as mining. One of the most common analogies that can be related to bitcoin mining is gold mining. Similar to other metal supplies in the world, there is a limited amount of bitcoins available for the potential users, namely 21 million. Bitcoin mining is the process of validating the current bitcoin transactions, known as blocks, and adding them to the record of previous block transactions, known as block chain.
To begin the mining process, the computers are given a complex mathematical problem to solve every ten minutes, which results in generating a block that contains the latest transaction data. Each one of these created blocks, contains a hash of the previous block and is placed in a linear chronological order and stored in the database permanently. A hash is simply a mathematical algorithm that takes an input and converts it into an output. Bitcoin miners will compete to solve these mathematical problems and whoever solves the puzzle first, gets to put the block on the block chain, and earns bitcoins as a reward.
Legality
Bitcoin has been a revolutionary internet-wide payment system, which has become a matter of great public interest and as its popularity increased, the debate as to whether it is legal or not has intensified. Given its ability to be used anonymously and not be backed by any governmental authority, bitcoin has proven to be a major concern for many law enforcers and regulators. The primary concern related to bitcoin is its potential for money laundering and other illicit activities. Due to the ease of transferring money between countries without any prior monitoring, money laundering presents a key legal issue.
Provided that bitcoin offers the simplicity of moving money without having to go through a central authority, it has been highly praised by criminals who perform illegal transactions without leaving any trace. However, given the bitcoin’s popularity among these notorious groups, many countries have passed laws which limit the use of bitcoin under a certain legal framework. In 2013, Silk Road, a secret marketplace for illegal products and services in the ‘deep web’, was targeted and shut down by the FBI. One could purchase anything from drugs to firearms without being traced. Bitcoin was the only acceptable payment on Silk Road. After the FBI shut down their website, they seized around $3,6 million worth of bitcoins, which is considered as the largest seizure of bitcoin to date. Stories like that of Silk Road associate bitcoins with illegal activity. However, whether illegal or not, bitcoins have grabbed the public’s attention so far.
Bitcoin “Governing without governance”
Ever since the payment system has taken the lead in the world financial system as a medium of exchange, it has undergone major challenges in regards to the government economic policies and other financial institutions requirements. Generally speaking, the payment system has taken different forms from large circle stones, cattle, metal coins, and leather money to modern coins, paper currency, credit cards and digital currency. Considering the latest financial crises, it is not unusual to witness the emergence of alternative payment systems, aimed to facilitate the exchange of goods and services and establish a payment system that is acceptable by the society. The principles of governments and financial institutions are tightly linked with the centralized concepts and approaches. Since the medieval times, governments have supported and reinforced the idea of a centralized financial system with the purpose of increasing efficiency, direct state control and consistency with governmental planning. However, the appearance of a digital currency, particularly bitcoins in 2009, has revolutionized the traditional economic philosophy of centralized financial systems, whereby the central bank i.e., the US Federal Reserve Bank, has direct control over other financial institutions.
Thus, the bitcoin falls under the right wing of libertarianism values, which aim at downsizing the control of governments on the state economy. In other words, Bitcoin represents a modern decentralized digital currency that undermines the consolidated behavior of government and central banks. Further, bitcoin provides an antagonist standpoint of the centralized system, in terms of “governing without governments,” indicating a shift of political resources while relying heavily on technology. Indeed, bitcoins are not controlled by any central authority institution; they are rather defined by the bitcoin protocol, implying the fixed rate of money supply in the market. In addition, bitcoins do not serve as the lender of last resort or pose any future risk of hyperinflation in the market; however, there is a risk of hyper deflation at the later stages of bitcoin evolution. In addition, bitcoins are highly volatile because there is a limited amount of bitcoin supply, while the demand increases on a daily basis.
The bitcoin governance is mainly based on the blockchain; whereby the interaction between technology, computers, and people involved in the communication network occurs. The public blockchain is an independent system of communication, where the rules and incentives are established on the general agreements among users in the bitcoin network. There is no intermediary in the chain network of communication between bitcoin users. In November 2016, the Bank of International Settlements (BIS) has questioned the ability of banks to exert control over the world economy, considering that this may put the power of central bank institutions at risk.
In addition, the decentralized system of bitcoins has transformed the conventional structure of centralized systems regarding the lack of restrictions in international money transactions, inexistent transaction fees, completely transparent and quick transfers at the users’ convenience. In terms of security, bitcoin is based on the premises of an encrypted structure aimed at emphasizing the role of cryptocurrencies in the world financial system and ensuring a safety economic culture. Nevertheless, it is to be seen how governments and central bank institutions cope with cryptocurrencies in the near future.
Bitcoin Ups and Downs
The price of bitcoins is highly volatile and there is no centralized exchange for it. Since its conception in 2009, bitcoin’s price has increased tremendously compared to its initial price of below $0.14. As the currency gained a viral traction, its high demand relative to its limited supply, caused an upward shift in its price until it reached “dollar parity”, meaning it hit a $1.06 per bitcoin.

Seeing its growth potential, numerous magazines wrote about this new cryptocurrency causing its price to rise up to $9 per bitcoin. In 2011, the market value for all bitcoins in circulation was around $130 million. However, as bitcoin’s price was constantly rising, disturbing events began to bedevil its popularity. Some users started claiming that substantial amounts of bitcoins had been stolen from their computers stimulating a massive sell-off, thus lowering the price of bitcoin. Provided this massive fall, the market forces conspired to prevent the scheme. The speculators flocked to take advantage of such low prices causing an immediate increase in the price of bitcoin.
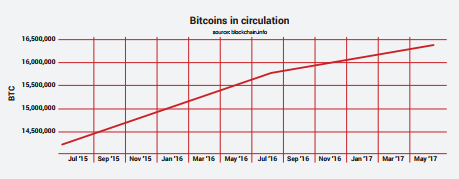
The price of bitcoin has been subject to major ups and downs and as its supply is being soared, the demand for bitcoin is constantly exceeding its supply. Analyzing bitcoin trends throughout years, it can be noticed that bitcoin has moved from a stage of ‘sin’ enterprises to a steeper progression of ‘legitimate’ enterprises. The increase in the number of bitcoin ATMs from 538 in January to 838 in November 2016, shows that the price of bitcoin is expected to increase to $3000, a peak that has not been reached so far.
The impact of Bitcoins in the Global Economy
Is the current global economy moving towards a digital-based economy? Truly, that’s uncertain. There is an ongoing debate between the supporters and opponents of the digital-based economy, in regards to the role and impact of cryptocurrencies in the world economy. The supporters of the digital-based economy argue that cryptocurrency is the greatest innovation in the economic system because of its decentralized nature of operation that implies profound changes in the state economic policies, reduction of financial instabilities and inflation risks.
Recently, the Prime Minister of Malta, Joseph Muscat has stated for Malta Profile that “other European regulators may be wary of the new technology, but the fact is that it’s coming. We must be on the frontline in embracing this crucial innovation. We must be the ones that others copy, and Europe should be the bitcoin Continent.” The direct impact of bitcoins in the global economy is related to the payment system, in regards to the improvement of efficiency in the international transaction system, emphasizing self-independence, built-in scarcity and increased security. Unlike, the conventional ‘pull’ payment system, bitcoins denote to the ‘push’ payment system where the transaction is initiated from the payer’s side to the payee’s side. Moreover, the high interest rates of 9% in international banking transactions have affected most of the business and individuals involved in the working force.
However, bitcoin generates lower transaction fees, rarely to 1% of its transaction value; providing a signal of improvement in the transaction system, while encouraging individuals to embrace digital currencies. Nowadays, the trend of bitcoins has surpassed its planned limits of expansion, whereby in the first quarter of 2017, the transaction volume of bitcoins was $260 million or $180,000 per minute according to the Blockchain Luxembourg S.A.R.L. This volume of transactions indicates a growth in international financial transactions, and an increase in interactions and usability among different profile users. More than 75,000 merchants, including Etsy, Dell Computers, Expedia, Zynga, WordPress, Overstock, Amazon and Microsoft have started to accept bitcoins in exchange for their goods and services. Perhaps, in the near future bitcoins could become a genuine payment system that will be accepted by business, customers and the society.










