In a world of constant change, risk management is increasingly viewed as a means of improving the likelihood of success in the challenging task of managing the organization’s reputation and stakeholder’s interest. The unmanaged risk is the greatest source of waste, whereas a result thousands of jobs and expertise get lost, and many great companies fail to survive; consequently, standards are considered to be very beneficial since their implementation allows the organizations to compare their existing risk management practices with internationally recognized benchmarks. The ISO 31000 standard should be the first step that shows organization’s commitment to ensuring the evolvement of risk management. Therefore, it serves as a guide for identifying and prioritizing important risks. Risk management process is applicable to organizations of all sizes and types, and it is intended to be tailored to meet the varying needs of the organization.
Key Points for an Effective Risk Management Plan
Understanding the value of risk management helps organizations to achieve higher levels of efficiency, flexibility, and transparency. An effective Risk Management includes the following:
- Creates shareholders value by linking risk with organizational performance;
- Established common objectives and clear understanding of the effect of the potential risks;
- Involvement of organization’s members in crucial decision-making processes;
- Effective risk assessment process and continuous improvement;
- Increased risk awareness, and incorporation of risk into the organization’s culture;
- Appropriate risk management measures that continuously facilitate the detection and updating process of the risks and relevant actions to treat such risks.
The Purpose of ISO 31000
ISO 31000 specifies principles and guidelines of risk management to identify, assess and mitigate risks faced by organizations. It is designed to help organizations ensure conformity with legal and regulatory requirements and international norms. In addition, it increases the possibility of achieving organizational objectives, improves the identification of threats and opportunities, and helps an organization in treating the risks and minimizing the negative impact. The standard consists of two related documents: ISO Guide 73 and ISO/IEC 31010. The ISO Guide 73 provides definitions and terms that are linked to Risk Management while ISO/IEC 31010 entails risk assessment techniques.
This standard provides guidance on how to appropriately identify and manage risks in order to minimize losses and maximize the opportunities. It outlines the principles for effective risk management and a framework for supporting the implementation of continual improvement.
Risk management capabilities can directly affect the costs incurred by the organization, as well as the customer value creation. By effectively managing the uncertainties which occur in the business environment, those capabilities can turn into a source of competitive advantage.
The ability to respond faster to unforeseen events and the willingness to seek greater risks which competitors are not capable of undertaking, gives the organization the opportunity to enhance future profits. Furthermore, risk management is considered as a core aspect of project management process, as it is viewed as a promising tool for protecting organization’s reputation and brand, and improving the sustainability and resilience of the organization.
John Roos a Project, Program and Quality specialist stated “ISO benefits exceed the simple satisfaction of having just another certificate on your wall. If such benefits are recognized and acknowledged, the management will provide approval and support to ISO as this ensures the use of professional methods and techniques, and simultaneously a high quality standard“.
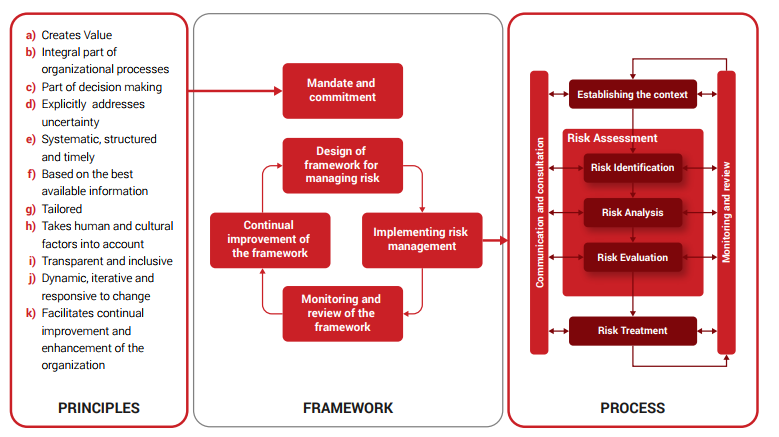
A structure preview of the ISO 31000
ISO 31000 consists of principles that may be considered as the cornerstone based on which organization’s success is built upon; a Risk Management framework comprising 5 components which ensure that the process for managing risk is fully integrated into the organization; and Risk Management processes that emphasize the necessity for active communication and consultation with internal and external stakeholders, and the continuous monitoring and review. The detailed components of the ISO 31000.
11 Principles of Risk Management
- Risk management creates and protects value
- Risk management is an integral part of all organizational processes
- Risk management is part of decision making
- Risk management explicitly addresses uncertainty
- Risk management is systematic, structured and timely
- Risk management is based on the best available information
- Risk management is tailored
- Risk management takes human and cultural factors into account
- Risk management is transparent and inclusive
- Risk management is dynamic, iterative and responsive to change
- Risk management facilitates continual improvement of the organization
Risk Management Framework
- Policy and Governance
- Program Design
- Implementation
- Monitoring and Review
- Continual Improvement
Risk Management Process
- Communication and consultation
- Establishing the context
- Risk identification
- Risk analysis
- Risk evaluation
- Risk treatment
- Monitoring and review
The ISO 31000 Revision
The ISO 31000 Revision has a clearer objective: make things easier and simpler for the user. ISO/DIS 31000:2017 uses plain language to define the basics of risk management with the expectation that the reader will find it easier to understand. The standard is intended to be more concise, understandable and comprehensible to the user.
To avoid potential complications, it has been decided to reduce the terminology in ISO/DIS 31000:2017 to the basic concepts which are closely related to risk management, which appears in ISO Guide 73 – Risk management – Vocabulary. An important aspect of the progress within the standard is the value of human and cultural elements, which facilitates attainment of the organization’s objectives. Nevertheless, the main objective set by the ISO 31000 standard remains the same – to integrate risk management into a strategic and operational management system.
It is important to note that the ISO/DIS 31000 has been approved by the majority, and the next meeting will take place in Sunnyvale, California from July 10th to July 14th.
Carlos Horna Vallejos committee member at ISO/TC 262 stated: “In my opinion, the main change is the simplicity, an easier to understand wording to extend the use of the standard. We have new management systems with a focus on risk management (all ISO requirements), greater impact on GRC and compliance, and this standard will help us to understand how to deal with uncertainty to adequately address risks (positive, negative or both) for achieving our objectives.”
The Value of ISO 31000
ISO 31000 principles and guidelines may not only be employed to catalyze the professionalization of project risk management, but also to enable organizations to conduct coordinated research on the effectiveness of risk management measures and practices; thus, in so doing provide the necessary protection for the organization. ISO 31000 adoption will trigger the following benefits:
- Increased probability of reaching organization’s objectives
- Enhancement of proactive activities
- Improved ability to identify and treat risks within an organization
- Enhanced capacity to identify opportunities and threats
- Higher conformity with legal and regulatory requirements and international norms
- Improved shareholder’s confidence and reliability
- Improved financial reporting
- Improved governance
- Consistent basis for decision-making and planning
- Successful allocation of resources for risk treatment
- Improved coherence, effectiveness, and efficiency of operations within organizations
- Improved environmental protection as well as health and safety performance
- Lower financial volatility
- Establishment of a resilient organizational culture
Having recognized risk management as a promising tool for improved economic performance and professional reputation, it is of crucial importance to adhere to principles of standards such as ISO 31000. This standard is viewed as an impactful body of knowledge for the project risk-management community. PECB offers its expertise in multiple fields, including ISO 31000 courses, where it provides a shared understanding of best practices with the ultimate goal of enhancing risk management effectiveness. For further information, please visit PECB Certified ISO 31000 training courses.