API integrations have become pivotal for enabling seamless communication between disparate systems and applications in the rapidly evolving information technology landscape. The surge in artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities has further propelled the adoption and proliferation of APIs, rendering them indispensable in modern IT infrastructures. I will explore the factors driving the increase in API usage, the role of AI in fueling this growth, the security threats associated with API integrations, and the strategies and frameworks necessary to mitigate these threats. Additionally, I will outline a roadmap for ensuring secure and sustainable API integrations in the future.
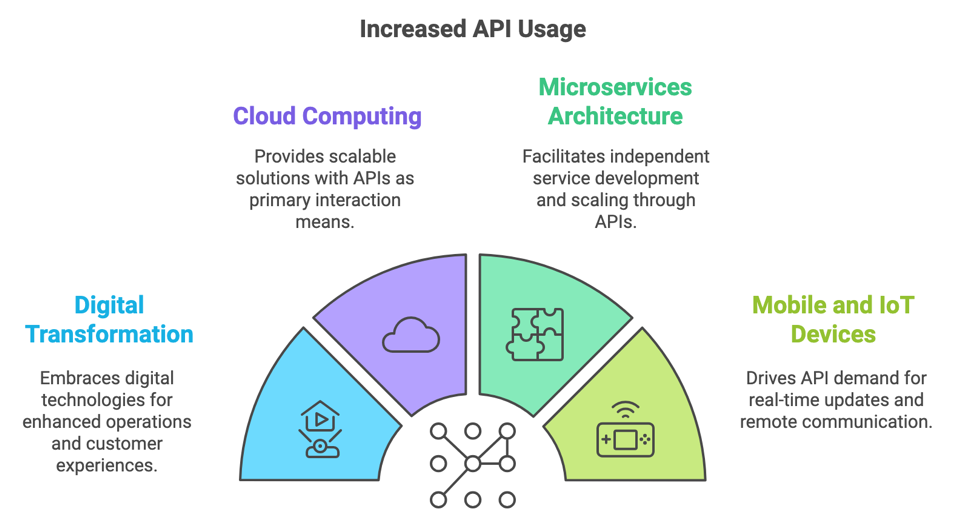
Factors Leading to Increased API Usage
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation has significantly driven increased API usage. Organizations across various industries embrace digital technologies to enhance operations, improve customer experiences, and maintain competitiveness. APIs facilitate this transformation by enabling seamless communication and data sharing between systems. For example, e-commerce platforms use APIs to integrate with payment gateways, logistics providers, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, creating an efficient digital ecosystem.
Cloud Computing
The rise of cloud computing has also contributed to the surge in API usage. Cloud services offer scalable and flexible solutions accessible over the internet, with APIs as the primary means of interaction. APIs enable users to manage cloud resources effectively, such as provisioning virtual machines and deploying applications through programmatic interfaces.
Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture has revolutionized application development and deployment by breaking down applications into more minor, independent services that can be developed and scaled independently. APIs are the communication bridges between these microservices, facilitating data exchange and functional coordination.
Mobile and IoT Devices
The proliferation of mobile devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) has fueled demand for APIs. Mobile applications rely on APIs to interact with backend services and provide real-time updates to users. Similarly, IoT devices use APIs to communicate with central systems for remote monitoring and control.
How Is AI Fueling API Growth?
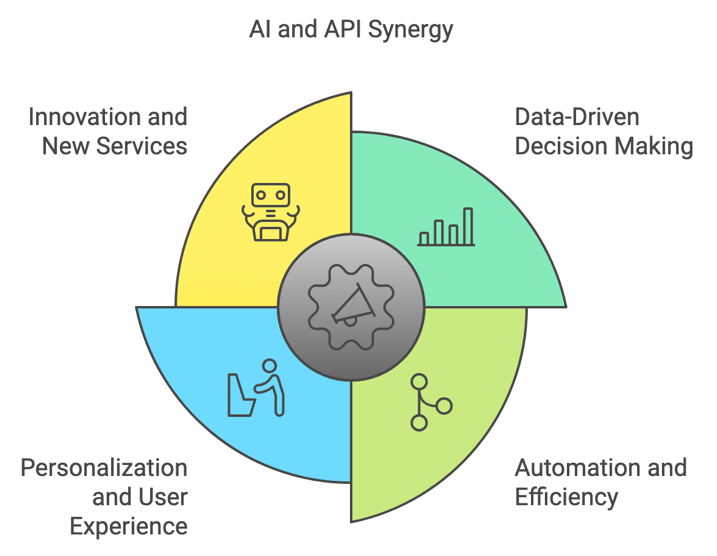
Data-Driven Decision Making
AI thrives on data, and APIs provide access to vast amounts of data from various sources. Organizations leverage APIs to collect, process, and analyze data, enabling AI algorithms to make informed decisions. For example, APIs can pull data from social media platforms, financial markets, and customer databases, feeding AI models that generate insights and predictions. This data-driven approach empowers businesses to optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Automation and Efficiency
AI-driven automation is transforming industries by streamlining processes and reducing manual intervention. APIs play a crucial role in this automation by enabling AI systems to interact with different applications and services. For instance, in the financial sector, APIs can automate trading processes, execute transactions, and monitor market trends in real-time. In healthcare, APIs can facilitate the integration of AI-powered diagnostic tools with electronic health records (EHRs), improving patient care and operational efficiency.
Personalization and User Experience
AI has the potential to enhance user experiences through personalized services, and APIs enable this personalization. By leveraging APIs, AI systems can access user data, preferences, and behaviors, tailoring services to individual needs. For example, streaming platforms use APIs to recommend content based on user viewing history, while e-commerce websites personalize product recommendations using APIs that analyze browsing and purchase patterns. This level of personalization not only improves user satisfaction but also drives customer loyalty and engagement.
Innovation and New Services
The synergy between AI and APIs is driving innovation and the creation of new services. APIs provide the building blocks for developing AI-powered applications that can solve complex problems and deliver unique value propositions. For instance, AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants rely on APIs to access information, process natural language, and provide real-time responses. Similarly, APIs enable the integration of AI capabilities, such as image recognition and sentiment analysis, into existing applications, opening up new possibilities for innovation.
Sustaining the Growth of API Integrations
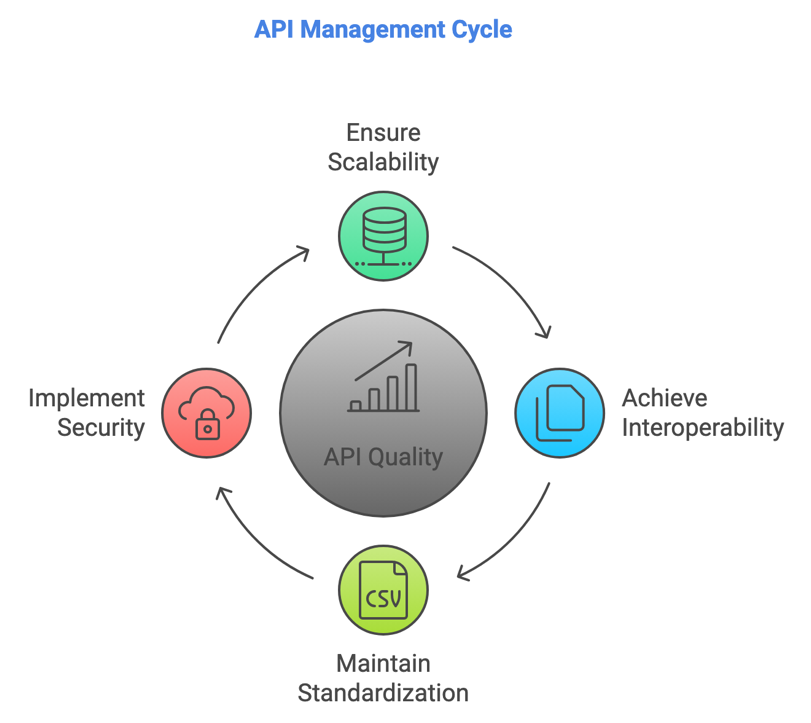
Scalability
As the demand for APIs continues to grow, ensuring scalability becomes paramount. APIs must be designed to handle increased traffic and usage without compromising performance. This involves implementing load balancing, caching, and rate-limiting mechanisms to distribute the load and prevent API endpoint overloading. Adopting scalable infrastructure, such as cloud-based solutions, can help accommodate fluctuating demand and ensure seamless API performance.
Interoperability
Interoperability is crucial for the success of API integrations, as it ensures that APIs can work across different platforms, systems, and technologies. To achieve interoperability, APIs should adhere to industry standards and protocols, such as REST (Representational State Transfer) and GraphQL. Standardization simplifies integration efforts and promotes compatibility and reusability of APIs. Furthermore, providing comprehensive documentation and developer support can facilitate third-party developers’ adoption and integration of APIs.
Standardization
Standardization is essential for maintaining consistency and quality in API development and usage. Organizations should establish guidelines and best practices for designing, documenting, and versioning APIs. This includes defining naming conventions, data formats, and error-handling mechanisms. Standardization improves the developer experience and enhances the reliability and maintainability of APIs. Additionally, participating in industry initiatives and adopting widely accepted standards can foster collaboration and interoperability within the API ecosystem.
Security
Security is critical to API integrations, as APIs often expose sensitive data and functionality. Implementing robust security measures is essential to protect API endpoints and prevent unauthorized access. This includes using authentication and authorization mechanisms, such as OAuth and JWT (JSON Web Tokens), to ensure that only authorized users and applications can access APIs. Encryption should be employed to protect data in transit and at rest, and regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Security Threats in API Integrations
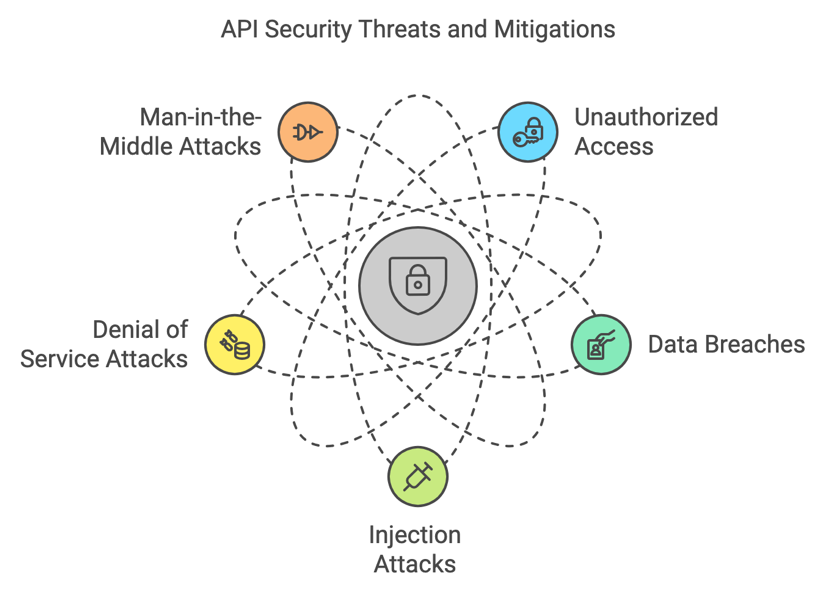
Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access is a significant security threat in API integrations, as it can lead to data breaches and unauthorized actions. Attackers may exploit weak authentication mechanisms or API endpoint vulnerabilities to access sensitive data and systems. Organizations should implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to mitigate this threat, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC). Monitoring and logging API activities can also help detect and respond to unauthorized access attempts.
Data Breaches
Data breaches are a significant concern in API integrations, as APIs often handle sensitive and confidential information. Insecure APIs can expose data to unauthorized parties, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. Organizations should implement encryption to protect data in transit and at rest to prevent data breaches. Data minimization practices should also be adopted to limit the amount of sensitive data exposed through APIs. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments can help identify and address potential weaknesses in the API.
Injection Attacks
Injection attacks, such as SQL and command injection, pose a significant threat to API security. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in API endpoints to inject malicious code or commands, potentially compromising the underlying systems and data. To mitigate injection attacks, organizations should implement input validation and sanitization mechanisms to ensure that APIs process only valid and safe data. Additionally, parameterized queries and prepared statements can help prevent SQL injection attacks.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks aim to disrupt the availability of API services by overwhelming them with excessive traffic or requests. These attacks can render APIs inaccessible to legitimate users, causing significant disruptions to business operations. To mitigate DoS attacks, organizations should implement rate-limiting and throttling mechanisms to control the number of requests that can be made to API endpoints. Additionally, deploying Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection services can help detect and mitigate DoS attacks.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks involve intercepting and tampering with API communications between clients and servers. Attackers can eavesdrop on sensitive data, modify requests and responses, and impersonate legitimate parties. To prevent MitM attacks, organizations should use Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt API communications and ensure the authenticity of servers and clients. Additionally, implementing certificate pinning and mutual TLS (mTLS) can provide an additional layer of security against MitM attacks.
Mitigation Strategies
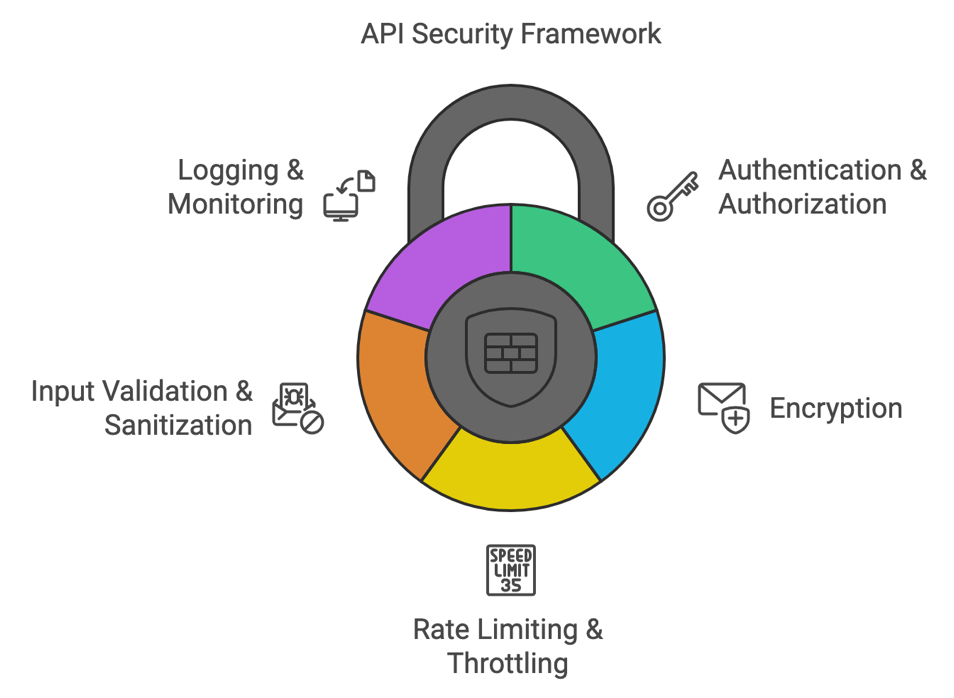
- Authentication and Authorization: Implement robust mechanisms using industry-standard protocols like OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect.
- Encryption: Use TLS to encrypt communications and ensure confidentiality and integrity.
- Rate Limiting and Throttling: Control request volumes, preventing abuse, or excessive traffic.
- Input Validation and Sanitization: Validate inputs, ensuring conformity, safety, and reducing injection risk.
- Logging and Monitoring: Continuously monitor and log activities, detecting and responding swiftly against suspicious actions.
- API Gateway: An API gateway manages and secures API traffic, enforces policies, and provides a single entry point.
- Regular Audits and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular security and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities
Frameworks to Follow
- OWASP API Security Top 10: Provides guidelines on mitigating critical security risks associated with APIs.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Offers recommendations for managing cybersecurity risks effectively.
- ISO/IEC 27001: International standards ensuring systematic information security management.
- GDPR/CCPA Compliance: Adhering regulations safeguarding personal data privacy rights.
- CSA Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM): This framework provides a detailed control framework for cloud security, which is essential for APIs hosted in the cloud.
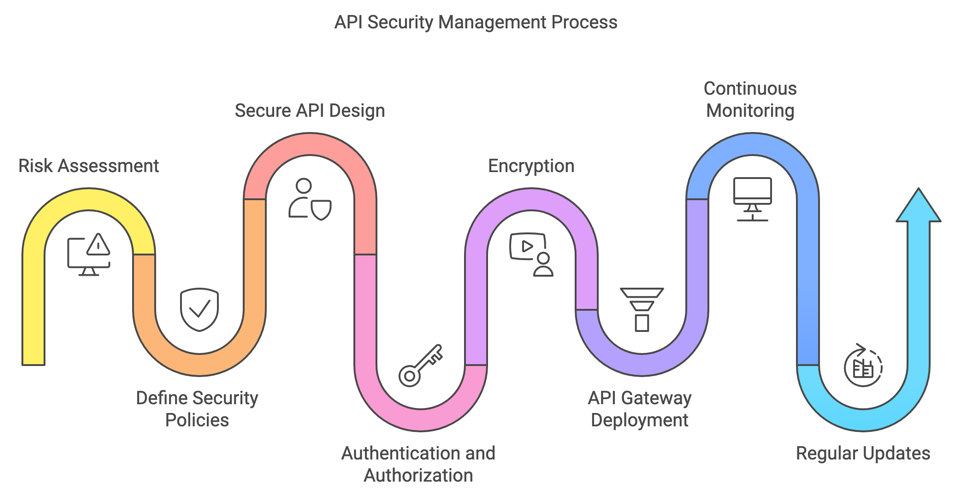
Roadmap for Secure API Integrations
- Assessment and Planning:
- Identify Assets: Catalog all APIs and their associated data flows.
-
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Define Security Policies: Establish security policies and procedures based on identified risks and industry best practices.
- Implementation:
- Secure API Design: Design APIs with security in mind, incorporating principles like least privilege and defense in depth.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implement robust authentication and authorization mechanisms.
- Encryption: Ensure data is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
- API Gateway Deployment: Deploy an API gateway to manage and secure API traffic.
- Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring to detect and respond to real-time security incidents.
- Regular Updates: Keep all software and libraries updated to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain an incident response plan to quickly address security breaches.
- Review and Improvement:
- Regular Audits: Conduct security audits to ensure compliance with security policies and standards.
- Penetration Testing: Perform regular penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop to improve security measures based on continuous audit and testing results.