Things have moved on from the telephone and fax machines. Thanks to the internet, organizations can enjoy innovations around communication. Those looking for savings and flexibility are increasingly using technologies powered by the cloud. Prompted by an increase in demand for remote working solutions, in 2021 42% of EU companies said they’ve used such technologies.
However, communicating online poses risks to data security. Cybercriminals are constantly looking for vulnerabilities to exploit. Happily, cloud communications service providers are here to help. We are going to answer the question “what is cloud communications?” Additionally, we will examine how cloud technologies can bolster data protection.
The Cloud: A Definition
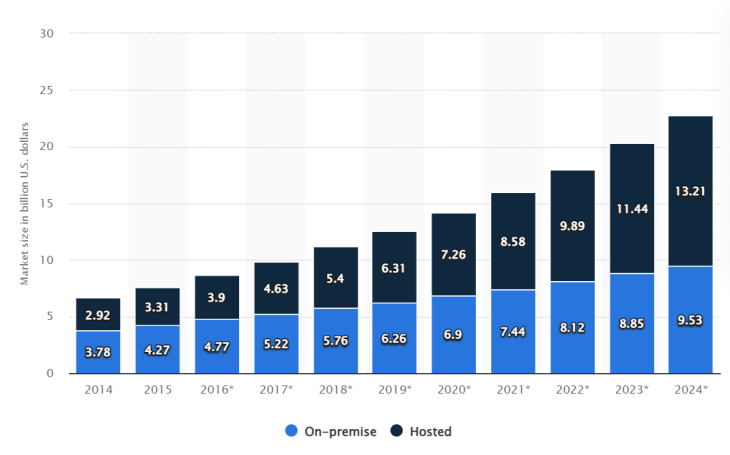
The cloud refers to servers that run applications for users to access remotely. They do so via the internet. This is advantageous because organizations since there is no need to invest in expensive hardware or software. You may wish to learn more about on-premise vs cloud.
Many different kinds of applications can be used through the cloud. Some examples are word processing, data analytics for communication service providers, and yes, communications tools. Access is granted through a subscription or, depending on the service, may even be free.
Reduced cost is not the only benefit offered by the cloud. It also boasts improved functionality. For example, Google Docs allows multiple users to access and edit the same document. This is a boon for businesses that want a collaborative workforce across multiple locations.
What is cloud communications?
Organizations increasingly use the cloud to communicate via internet protocol. This allows for the exchange of data, video, or voice communications. Cloud communications are also known as unified communications (UC). This is due to the ability to communicate in these different mediums.
A service provider takes care of the UC infrastructure, operation, and offers support. Organizations pay a subscription, eliminating the need for large upfront investments. The use of these kinds of services saves organizations on their phone bills. Furthermore, they offer increased flexibility and scalability. It is easier to add additional users as they can utilize any device that can access the internet. This means organizations with a bring-your-own-device policy avoid the need to invest in extra hardware.
Examples of cloud communication
- VoIP
- Video conferencing
- Text messaging
- Data transfer
In the following section, we will take a closer look at each of the examples listed above.
Voice over internet protocol (VoIP)
VoIP is a replacement for POTS. You may be wondering “What is POTS?.” It stands for Plain Old Telephone Service. You know, copper wires powering and connecting users’ communication tools. Organizations require more flexibility than POTS can provide. This is being driven by higher demand for remote working solutions.
How does it work? Service providers offer Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunking. It allows VoIP connectivity between phone systems and the public network. This creates a private branch exchange (PBX). It then converts voice communications into data that can be sent via the internet.
Almost any internet-connected device can be used to communicate in this way. This enables businesses to use whatever device is most suitable for them. Moreover, it allows for the implementation of a bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policy, as we mentioned before. It is another way to improve cost efficiency.
Additionally, it allows for a mobile workforce. Employees can communicate with colleagues and clients wherever and whenever needed. This is a major boost to operational flexibility.
By using a cloud-based service for VoIP, managers are able to monitor call activity and organize user accessibility. Businesses wishing to record calls may need employees to sign a waiver. Using a waiver template makes this an easy process and ensures your business and your employees are fully protected.

Video conferencing
Nothing beats face-to-face interaction for a truly collaborative workplace. Cloud services allow for high-quality video conferencing. This enables disparate teams to communicate with the added value of seeing who they are talking to. This is advantageous because facial expressions and body language say as much as words do alone.
Video conferencing also provides a set of features not available through VoIP. Screen sharing, for example, allows users to show important information to other participants. Also, video conferences can be recorded. This is great if a stakeholder is unable to join the conference but needs to see the call at a later date.
When organizations use a cloud-based video conferencing solution, they get all the flexibility that cloud VoIP offers. That means users can participate from anywhere and use whatever device is best for their purposes.
Text messaging
Sometimes it is unnecessary to make a phone call or get on a video conference. When an employee wants an answer to a simple question, a text message will do. Cloud services allow for SMS messaging between colleagues and clients. This is often far more efficient than a call or even an email.
SMS through the cloud is more secure than traditional text messaging. This is thanks to complex encryption. If users wish to send pictures or other media via traditional SMS then the costs can increase. This is not the case when using a cloud-based messaging app.
Data transfer
This is not just a communication tool, it is a complete cloud collaboration service. Teams working in a connected workplace need to be able to share data, as well as communicate. Again, this needs to be possible when teams are working remotely. The cloud makes this possible.
Something we have not looked too closely at yet is cybersecurity. We will go into more detail later but it is worth noting now. Users can securely share data with colleagues and customers. Cloud-based communications service providers can automatically back up data. In the event of a data breach or disaster, vital business data is secured off-site.
Data security risks
There are risks when organizations operate online. Organizations may be choosing a winner in the battle of softphone vs desk phone, for example. Which is best for their purposes? They must also consider the data security implications. The same goes for any online activity.
Threats to look out for include:
- Phishing scams
- Malware
- Data theft
- Ransomware
- DDoS attacks
The best cloud communications service providers employ robust security practices. This means organizations can use their services with total peace of mind. Organizations will still need to know what they can do to protect their data. We will return to this later. For now, let us discover how providers keep business data secure.
Physical security
To the user, cloud services can appear ethereal. Indeed, that is part of the magic of cloud-based services. However, it is underpinned by physical infrastructure. Servers must be housed securely somewhere on terra firma. They are housed in data centers that businesses access via the internet.
Data centers are a target for cybercriminals. Also, they are vulnerable to disasters, such as fire or flooding. Service providers take these risks seriously and prepare accordingly.
- Access is limited to authorized personnel only.
- Data centers are surveilled by security personnel and CCTV.
- Clustered and distributed infrastructure means data is housed in multiple data centers should one go down.
- Security logs are kept so providers can track personnel’s comings and goings.
- Expert personnel maintain hardware at data centers.

Systems security
If an organization relies on the cloud for business communications then it is vital that providers keep their service up and running. This requires a host of measures to ensure systems are secure.
- Data backups keep business information safe, ensuring business continuity.
- Firewalls automatically protect against malicious attacks.
- Systems are monitored for unusual activity.
- Access to systems is tightly restricted.
Application security
The applications that providers offer need their own layers of security. Data centers and systems can be locked up tight, but a cybercriminal could breach security through APIs. Thus, providers must offer tools for authentication and application security.
- TLS (transport layer security) encrypts data when traveling between users and the servers.
- Multi Factor authentication verifies logins via SMS or email when the user logs in with their username and password. This is part of the future of passwords and data security.
Data security
UC allows for the transferring and storage of files in the cloud. It is, therefore, essential that security measures are taken to protect organizational data. Personnel information, customer details, and intellectual property are all at risk. Also, organizations will have to maintain HIPAA Compliance to protect private medical information. Happily, service providers have a litany of tools at their disposal.
- Data is encrypted to ensure that it is secure. Encryption uses complex mathematics to scramble data so only authorized users can access it.
- Access is limited to authorized personnel only.
- Businesses have control over authorization and can manage it remotely on any device.
- Privacy policies ensure providers are bound to an agreement to take care of the user’s data.
What steps can users take to help data security?
Cloud communications service providers possess many tools to help data security. As any guide to data security will tell you, users also have a part to play. Businesses have a responsibility to take due care of customer data. This is not just the right thing to do, it is backed up with legislation.
Following are some examples of what businesses can do to bolster their data security.
- Use strong passwords, and change them regularly.
- Use good practice when dealing with emails. Verify senders’ addresses and do not open attachments from unknown sources.
- Only use highly rated and trusted cloud service providers.
- Backup data to the cloud and encrypt it.
- Be proactive in managing user accessibility. Only grant access to data for those that require it.
- Conduct a cybersecurity risk assessment. This process helps businesses identify their risk exposure. They can use these insights to put appropriate measures in place.

Cloud communications are secure
We have answered the question “what is cloud communications?” and examined the advantages. Organizations can benefit from cost and efficiency savings by using cloud communications. Those that use a trusted provider will also have better data security. The trend for cloud-based business solutions is a growing one. Moreover, it is constantly improving data security for organizations and their customers.