Continuity of business operations in the event of a disruption is not only a concern for big corporations but also for every organization irrespective of its size or nature. For far too long, big corporations have invested in the implementation of continuity capability measures to ensure that they are prepared for, can respond to and recovery from, any disruption. Indeed, this initiative has seen to be successful for such corporations even in the midst of disruptions.
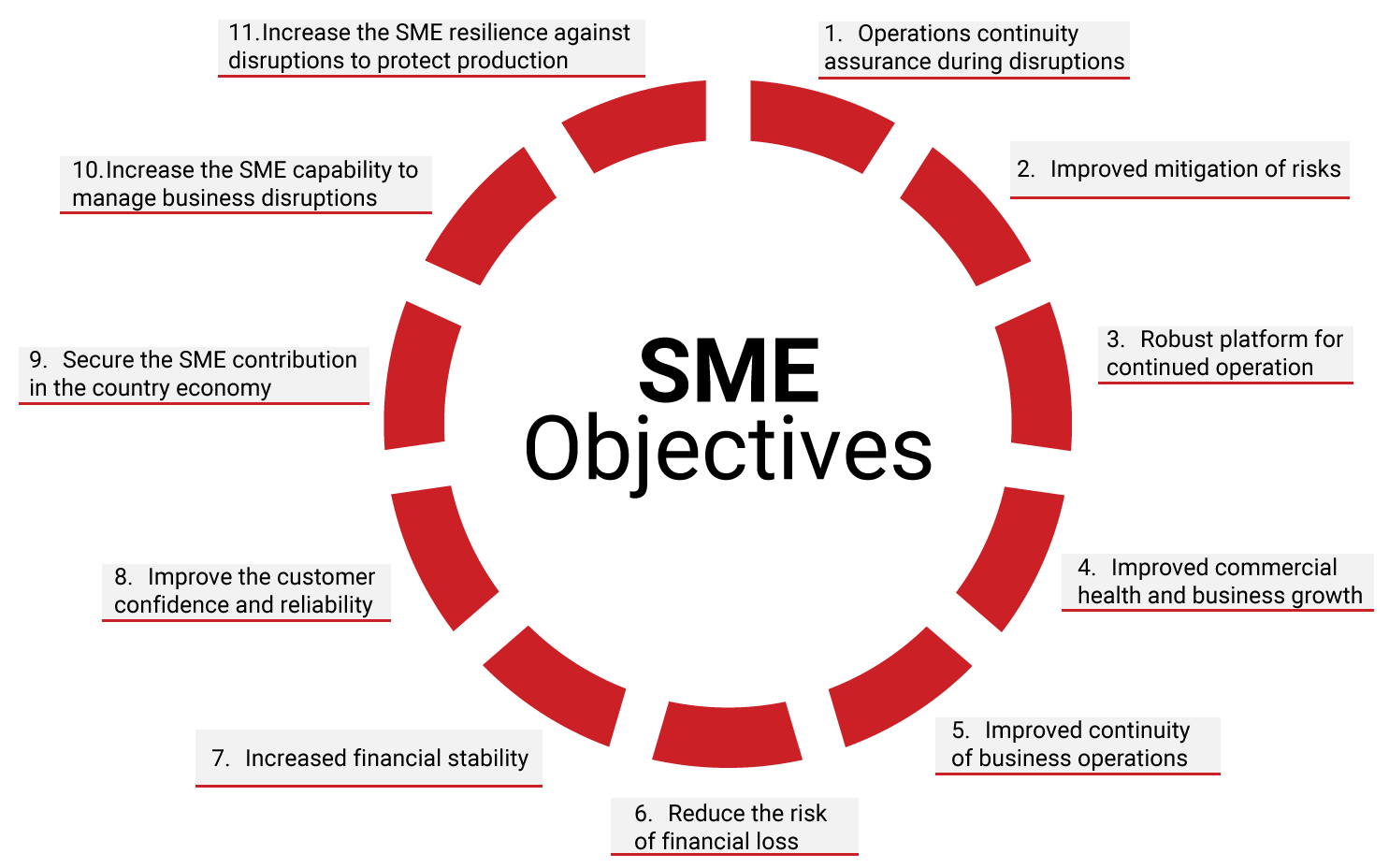
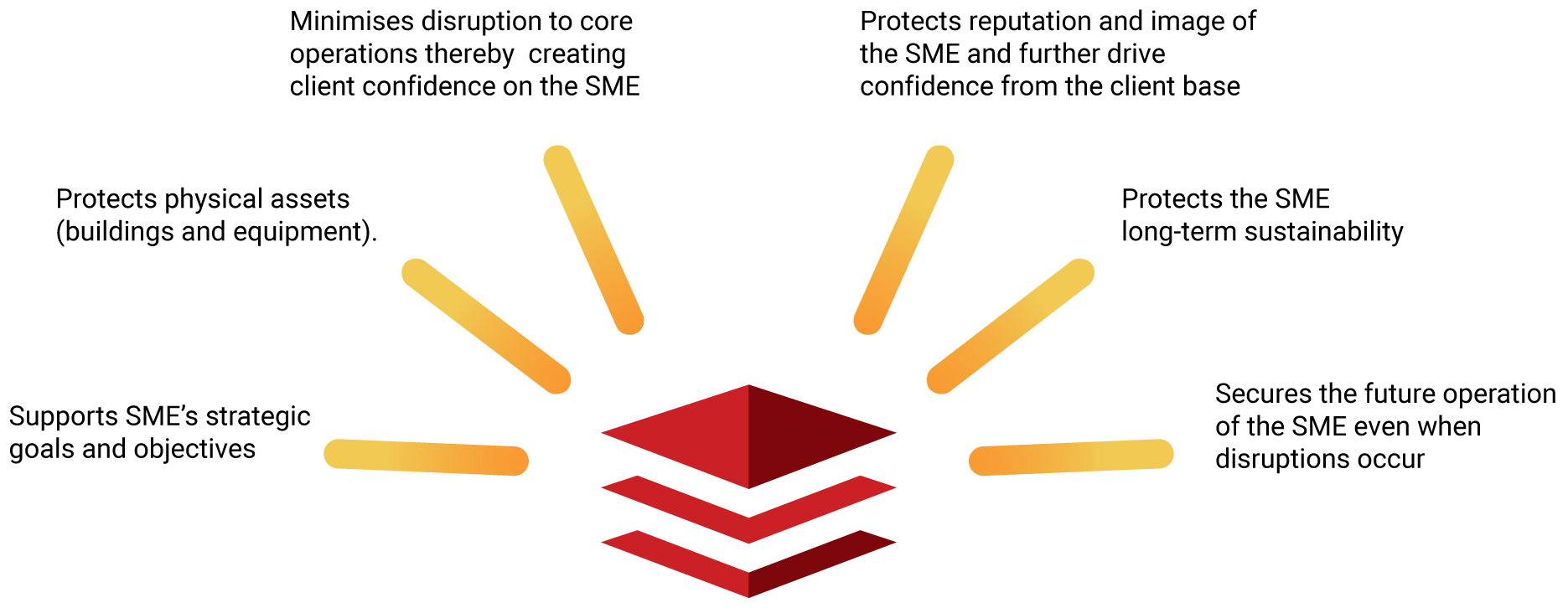
Implementation of a continuity management program by SME’s can, just like big corporations, yield similar results though SME’s stand to accrue even more benefits from its implementation. The following are amongst other the benefits that the SME’s stand to benefit:
Continuity Program implementation challenges for SME’s in the developing world
Whilst there are benefits of implementing continuity frameworks, such comes with challenges that the SME’s should convert to opportunities. It must be argued that these challenges are driven by varying differing factors that are not necessarily the same as the diversity from continent to continent, country-to-country etc. For most of the developing countries in general and Africa in particular, these challenges are shaped amongst others by factors such as, but not limited to:
Benefits of implementing BCM by SME
How can we optimize the implementation of Business Continuity Plans?
There is then a critical question to ask with an intention to guide and shape the orientation of the SME’s Continuity Programs “How can an SME implement and improve its continuity capability in the midst of the aforementioned challenges”.
Challenges faced before, during and after the implementation of the Continuity Program present hidden opportunities that could propel an SME to improve its continuity capabilities. There are some critical factors that an SME should incorporate into the continuity program in line with the ISO 22301, being:
For the SME to ensure that the best value is derived from the continuity program, there is, therefore, a need to implement programs that drive the SME’s strategic objectives in an efficient manner to support the critical priorities. The set of defined strategies informed by the Business Impact Assessment should guide the SME in determining the continuity strategy for specific areas such as technology, supply chain, business processes, facilities etc.
In determining the continuity strategies, an SME focus on the ensuring that there is provision for:
- Secure and stable information processing facilities and office locations with adequate physical and environmental safeguards;
- Redundancy in identified information technology systems and applications;
- Maintained data-protection procedures and conducted regular backups of critical applications, platforms, configurations, and data with off-site rotation;
- Cases where external service providers are utilized, there should be multiple suppliers in order to limit a single point of failure in the event of a disaster;
- Constant monitoring of the external service provider continuity capability;
- The monitoring of the key critical business process against the key criticality determinants such the legislative requirements;
- The Formulation and documentation of emergency procedures considering the necessities of life;
- The Identification of an alternate site for the recovery of an operation within an acceptable distance from the primary site of operations.
Business Continuity Standardisation
Whilst acknowledging that BCM is still a new concept in the developing world, implementation of the program can be simplified without compromising the value embedded therein. Internationally recognized standards such as ISO 22301 provides a base upon which SME can derive the core principles for a robust BCM program. Core principles defined in ISO 22301 are critical to ensuring that the SME is guided from the implementation of the continuity strategies to the training of employees.
Deriving Value from BCM
Implementing a BCM program is argued essential, however, such does not complete the picture of resilience and continuity. Deriving value from BCM remains the major differentiator compliant SME and resilience SME. Value will be realised once the culture has been embedded into SME’s operations, employees are able to manage through an in-depth understanding of their responsibilities towards BCM; and even to a greater degree the SME being able to plan, design, develop and implement continuity strategies that are translated to resilience of the SME operations that conduct achievement of the objectives.
PECB
Regardless of many companies negligence towards Business Continuity planning, ISO 22301 (https://pecb.com/iso-22301-ms) has found application in a substantial number of organizations, while leading incident management and founding resilience. Besides, ISO 22301 courses have contributed to increasing the competence of individuals implementing and maintaining resilience within the organization.