The pursuit of excellence in the field of quality management is an ongoing journey for every organization. Every organization faces unique quality challenges, but what matters the most is how these challenges are identified, addressed, and resolved.
Nonconformity (NCR) reports are some valuable tools used to effectively cope with these quality issues. They have the potential to revolutionize quality control processes. By adopting the right approach and following a systematic process for nonconformity reports, organizations can enhance their quality management practices.
What is Nonconformance?
Nonconformance is a term used in quality management to describe situations where something does not meet established standards, processes, or other specifications. It can happen in different ways, similar to when a product has problems, a service does not meet expectations, or a process is not efficient.
Understanding Nonconformity Reports
NCR reports are detailed records used to document and communicate instances of nonconformance. They play an important role in quality management because they help organizations identify and address issues effectively.
When a nonconformity is identified, it is important to accurately document it. This includes recording essential information, such as what went wrong, where it happened, and when. By documenting these details, organizations can better understand the problem and its impact.
NCR reports also aim to uncover the root causes behind the issues by going deeper to find out why they happened in the first place. This analysis helps identify underlying issues and implement actions to prevent similar nonconformities from happening again.
The ultimate goal of NCR is to drive continuous improvement. By documenting, analyzing, and addressing nonconformance, organizations can enhance their quality control processes, meet customer expectations, and strive for excellence.
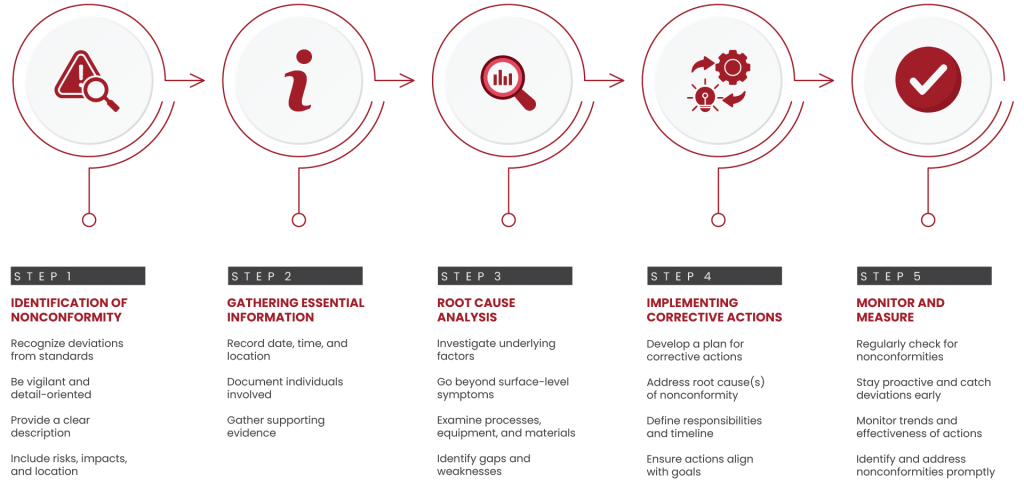
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Nonconformity Report
Step 1: Identification of Nonconformity
The first step in creating an NCP report is identifying the nonconformity itself. This means recognizing instances where products, services, or processes deviate from the established standards or requirements. During this step, it is crucial to be vigilant and attentive to detail in identifying nonconformities to ensure accurate documentation.
When identifying a nonconformity, it is important to provide a clear and concise description of what went wrong. Include specific details such as the nature of the nonconformity, any associated risks or impacts, and where and when it occurred.
Step 2: Gathering Essential Information
Once the nonconformity is identified, gather all relevant information related to the incident. This includes recording the date, time, location, individuals involved, and any supporting evidence. Accurate and detailed information is crucial for understanding the context and scope of the nonconformity, as well as for conducting a thorough root cause analysis.
To ensure clear communication and understanding, provide a concise but comprehensive description of the nonconformity. Clearly articulate the characteristics of the deviation and its potential consequences. This helps lay the groundwork for effective analysis and subsequent corrective actions.
Step 3: Root Cause Analysis
Conducting a root cause analysis is vital to understanding why the nonconformity occurred in the first place. This step involves investigating the underlying factors that contributed to the deviation from the standards. It is important to delve beyond the surface-level symptoms and identify the fundamental causes.
During the root cause analysis, examine various aspects such as processes, equipment, materials, and human factors. Identify any gaps or weaknesses that may have led to the nonconformity. This analysis helps to pinpoint the root cause(s) and provides insights into implementing effective corrective actions.
By understanding the root cause(s), organizations can address the core issues rather than merely treating the symptoms.
Step 4: Implementing Corrective Actions
Once the root cause of the problem has been identified, it’s time to develop a plan for resolving it. Corrective actions seek to identify and address the underlying reasons for nonconformity. This includes a clear identification of what needs to be done, who is responsible, and when it needs to be done.
In order to prevent a recurrence of nonconformity, we should make sure that corrective actions are practical, doable, and aligned with the goals of the organization. This could entail improving processes, fixing equipment, training employees, or even changing standard procedures
Step 5: Monitor and Measure
Monitoring and measuring involves regularly checking processes, products, or services for potential non-conformities.
It is important for organizations to follow this step in order to stay proactive, catch deviations early, monitor trends, and determine if corrective actions and preventive measures are effective. By monitoring key indicators and performance metrics, they can identify nonconformities early on before they become more serious.
Best Practices for Resolving Quality Challenges
- Communication and collaboration – Effective communication and collaboration are essential for resolving quality challenges. Establishing open channels of communication allows for seamless flow of information, ensuring that quality issues are promptly addressed.
- Proactive problem-solving – Empowering employees to take ownership of quality challenges promotes proactive problem-solving and continuous improvement. Provide training and resources to enhance their problem-solving skills, allowing them to contribute to the resolution of quality challenges.
- Technology-enabled reporting and tracking – In the digital age, leveraging technology is vital for efficient reporting and tracking of quality challenges. Implementing robust quality management systems or software enables streamlined reporting processes, ensuring accurate and timely capture of nonconformities.
To summarize, the importance of nonconformity reports cannot be overstated in achieving quality excellence. Managing them effectively is possible through a systematic approach to solving quality issues in organizations and driving continuous improvement.
Well-structured NCR reports enable effective problem-solving and successful monitoring of actions taken. They play a crucial role in maintaining and enhancing various management systems, including ISO/IEC 27001, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 45001, and more.









